Ethereum Gas – a term that might sound complex, but is essentially the backbone of every transaction on the Ethereum network. If you’re just starting your journey into the fascinating world of cryptocurrency, understanding
Ethereum Gas is crucial. It’s like learning the rules of the road before you start driving. In this guide, we’ll break down the concept of Ethereum Gas in a way that’s easy to grasp, even if you’re new to the world of digital currencies.
Key Takeaways
- Ethereum Gas Explained: Gas is the transaction fee paid on the Ethereum network. It’s the “fuel” that powers your transactions.
- Why It Matters: Without gas, your transactions won’t go through. It’s essential for keeping the network secure and efficient.
- Cost Implications: Gas fees vary based on network congestion – similar to how traffic affects fuel consumption in a car.
- Strategies to Minimize Fees: Learn when and how to transact to save on gas fees.
What is Ethereum Gas?
Imagine Ethereum as a giant, decentralized computer – and gas as the fuel it needs to operate. Each time you make a transaction, such as sending Ether (the currency of Ethereum) or interacting with a smart contract, you’re asking this massive computer to do some work for you. This work requires computational power, and just like any machine, it needs fuel to run. That’s where Ethereum Gas comes into play.
In technical terms, Ethereum Gas refers to the fee required to successfully conduct a transaction or execute a contract on the Ethereum blockchain. These fees are paid in Ether (ETH), Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency. But why is this necessary?
Why Do We Need Gas?
The concept of gas serves multiple purposes:
- Ensuring Network Security: By charging a fee for every transaction, it prevents malicious actors from spamming the network.
- Resource Allocation: Gas fees help in managing the computational resources of the network efficiently.
- Fair Compensation: Miners, who validate and add transactions to the blockchain, are compensated for their work through these fees.
For a deeper dive into Ethereum’s history and its foundational technology, you can explore more about Ethereum’s history.
How Are Gas Fees Calculated?
Every action on the Ethereum network has a cost, measured in gas units. Simple transactions, like transferring ETH, require less gas compared to more complex interactions, such as executing smart contracts.
The total gas fee you pay is a combination of these units and the gas price, which fluctuates based on network demand. To understand the nuances of these transactions, check out our comprehensive guide on Ethereum explained.
How Ethereum Gas Works
Understanding how Ethereum Gas works is like getting a grasp on the fuel economy of your car. It’s about knowing how much you’ll spend and why. Let’s break it down into simpler terms.
What are Gas Fees?
Ethereum Gas fees are like a toll you pay for using the network’s road. Each transaction you make on Ethereum, from transferring ETH to executing smart contracts, requires computational effort. This effort is measured in gas.
- Simple Transactions: Sending ETH might cost less gas.
- Complex Interactions: Executing a contract or using a decentralized application (DApp) requires more gas.
Factors Affecting Gas Fees
Several elements play a role in determining gas fees:
- Network Congestion: Similar to traffic during rush hour, more users on the Ethereum network can lead to higher gas fees.
- Transaction Complexity: More complex transactions need more computational power, thus more gas.
- Gas Limit: It’s the maximum amount of gas you’re willing to pay for a transaction. Setting it too low might result in failed transactions.
Strategies to Navigate Gas Fees
- Timing Your Transactions: Transacting during off-peak hours can save costs.
- Using Layer 2 Solutions: These platforms offer lower fees and are built on top of Ethereum.
- Monitoring Gas Trackers: Tools like Etherscan’s Gas Tracker help you decide the best time to transact.
To understand how Ethereum compares with other cryptocurrencies, consider reading about the differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Why High Gas Fees?
Sometimes, gas fees can skyrocket. This could be due to:
- Popular DApps or NFT releases driving up demand.
- Increased trading activity on decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
- Network upgrades or high user activity.
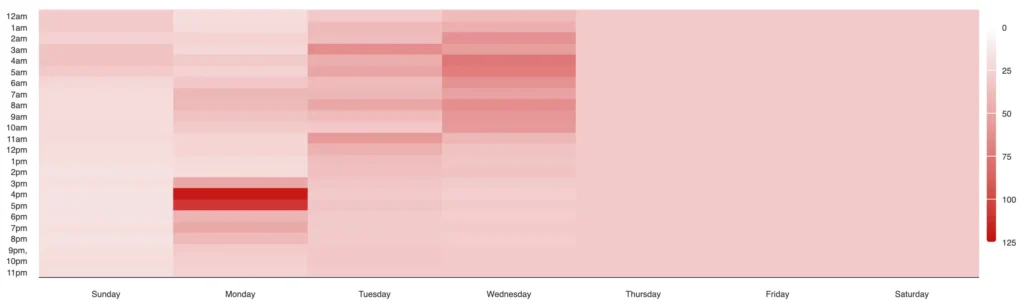
Understanding these factors helps you better plan your transactions and potentially save on fees.
Strategies to Minimize Gas Fees
Stepping into the world of Ethereum doesn’t have to mean high costs. Let’s explore how you can smartly minimize the gas fees.
Timing is Key
Choosing the right time to transact can make a big difference:
- Off-Peak Hours: Transactions during less busy hours (like when North America is asleep) usually cost less.
- Monitor the Market: Keep an eye on gas fee trends. Waiting a few minutes could mean a noticeable drop in fees.
Embracing Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 2 platforms are built on top of Ethereum and offer a more economical way to transact:
- Lower Fees: They handle more transactions at lower costs.
- Faster Transactions: Enjoy quicker processing times compared to the main Ethereum network.
Setting a Max Fee Limit
Control your spending by setting a maximum gas fee:
- Budget-Friendly: Specify the highest amount you’re willing to pay.
- Peace of Mind: Avoid surprises in transaction costs.
Utilize Gas Trackers
Tools like Etherscan’s Gas Tracker are invaluable for planning:
- Stay Informed: Monitor current gas prices.
- Strategic Transactions: Choose the best time based on real-time data.
For broader understanding, delve into the comparison of Ethereum with Bitcoin in Differences Between Bitcoin and Ethereum.
The Future of Ethereum Gas Fees
As the Ethereum network evolves, so do the dynamics of gas fees. Let’s look ahead and see what the future holds for these transaction costs.
Ethereum 2.0 and Its Impact
The much-anticipated upgrade to Ethereum, known as Ethereum 2.0, promises significant changes:
- Proof-of-Stake Model: Transitioning from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake aims to reduce the overall energy consumption and potentially lower gas fees.
- Increased Efficiency: Improved transaction processing capabilities are expected to ease network congestion.
Ongoing Upgrades
Ethereum is continuously improving. Regular updates are focused on:
- Network Scalability: Enhancing the network’s ability to handle more transactions.
- Fee Structure Adjustments: Implementing changes to make fees more predictable and fair.
Looking Ahead
As Ethereum grows, we can expect:
- Dynamic Fee Adjustments: Smoother adjustments in response to real-time network conditions.
- Broader Adoption: As the network becomes more efficient, it may attract a wider user base.
For additional insights into cryptocurrency investments, consider exploring Best Crypto to Invest in Long-Term.
Embarking on Your Ethereum Journey: What’s Next?
As we wrap up our exploration of Ethereum Gas, remember that understanding these fees is just the first step in your exciting cryptocurrency journey.
The world of Ethereum is vast and constantly evolving, offering endless opportunities for learning and growth.
Take Action and Dive Deeper
- Stay Informed: Keep up with Ethereum’s latest developments, especially Ethereum 2.0, to stay ahead of the curve.
- Experiment Wisely: Use your newfound knowledge to make informed decisions while transacting on the Ethereum network.
- Explore Further: Delve into other areas of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology. For instance, learn about the various cryptocurrency trading strategies or the impact of blockchain in different sectors like journalism.
Your journey into the world of Ethereum and cryptocurrencies is just beginning, and there’s much more to discover and experience. Embrace the adventure with curiosity and confidence, and watch as the world of digital currencies unfolds before you.
Frequently Asked Questions about Ethereum Gas
Here’s a table format FAQ section that addresses common questions about Ethereum Gas:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is Ethereum Gas? | Ethereum Gas is the fee required to conduct a transaction or execute a contract on the Ethereum blockchain. It compensates for the computational effort needed for the transaction. |
| Why are Gas fees required in Ethereum? | Gas fees ensure network security, manage computational resources, and fairly compensate miners for validating and adding transactions to the blockchain. |
| How are Ethereum Gas fees calculated? | Gas fees are calculated based on the complexity of the transaction and the current demand on the network. The total fee is a combination of base fee and priority (tip) fee. |
| What causes high Ethereum Gas fees? | High Gas fees can result from increased network congestion, complex transactions, high demand during popular DApp launches, or increased trading activity. |
| Can I control the amount I pay in Gas fees? | Yes, you can set a gas limit (maximum fee you’re willing to pay) and adjust the priority fee (tip) to control your expenses, but setting it too low may lead to transaction failure. |
| What changes are expected with Ethereum 2.0? | Ethereum 2.0 aims to transition to a proof-of-stake model, which is expected to increase efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and potentially lower gas fees. |
| How can I minimize my Ethereum Gas fees? | To minimize fees, transact during off-peak hours, use Layer 2 solutions for lower fees, monitor gas trackers for optimal timing, and set a max fee limit. |
| Where can I track current Ethereum Gas fees? | You can use tools like Etherscan’s Gas Tracker to monitor current gas prices and determine the best time for transactions. |




