In recent years, the phrase “blockchain technology in healthcare” has been buzzing around, promising a new era of digital innovation. This breakthrough technology, known for its role in powering cryptocurrencies, is stepping beyond digital coins into a realm that concerns us all – our health. Imagine a world where your medical records are secured yet easily accessible, where medication comes with a digital history, showing where and how it was made. Blockchain makes this, and so much more possible, offering a new lens to look through as we envision the future of healthcare.
The healthcare sector is a complex system with a myriad of challenges ranging from data security, privacy issues, to the management of medical supply chains. Blockchain, with its unique features of decentralization, transparency, and immutability, emerges as a game-changer to tackle some of these long-standing issues. Let’s delve into the heart of this topic and unfold the potential of blockchain in revolutionizing healthcare operations, making them more efficient, secure, and patient-centric.
Quick Takes:
| Key Points | Description |
| Enhanced Security | Blockchain provides a secure and immutable record-keeping system. |
| Improved Traceability | Real-time tracking of medical supplies and medications ensuring authenticity and compliance. |
| Efficient Data Management | Streamlined access and management of patient data with enhanced privacy controls. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Reducing operational costs through automated processes and reduced fraud. |

In the following sections, we will explore how the adoption of blockchain technology is not just a fleeting trend but a substantial stride towards a more transparent, secure, and patient-oriented healthcare ecosystem. Whether it’s about ensuring the authenticity of drugs, safeguarding patient data, or streamlining operational processes, blockchain technology holds the promise of redefining the contours of healthcare services. So, let’s embark on this insightful journey to understand how blockchain is set to reshape the healthcare industry, offering solutions that are as profound as they are transformative.
Blockchain Basics:
Understanding Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain is essentially a digital ledger, a decentralized database that is accessible to those who are part of its network. Each piece of information is stored in a block, and these blocks are linked or chained to each other, thus forming a blockchain. The significant traits of blockchain technology include:
- Decentralization: Unlike centralized systems where a single entity has control, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, making it inherently more secure and transparent.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to all network participants, promoting transparency while retaining privacy.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, thus ensuring the integrity of the data.
Blockchain technology is much more than just the backbone of cryptocurrencies. It’s a technology that promises to disrupt traditional systems and processes across various sectors, including healthcare.
Key Features Beneficial to Healthcare:
The healthcare sector is known for its stringent requirements for data security, privacy, and integrity. Blockchain’s core features align well with these requirements, making it a promising technology for healthcare advancements. The key features include:
- Security: With cyber-attacks on the rise, the security of sensitive patient data is paramount. Blockchain’s cryptographic security features ensure that data remains untampered and secure.
- Privacy: Blockchain can provide controlled access, ensuring that patient data is accessible only to authorized individuals.
- Traceability: Real-time tracking of medical supplies and drugs, from manufacturer to consumer, is crucial for ensuring authenticity and compliance.
With the healthcare sector being vast and complex, the integration of blockchain technology could simplify many processes, ensuring security, privacy, and efficiency. For a deeper understanding of blockchain technology, its functioning, and its various other applications, you can refer to How Does Blockchain Work: A Comprehensive Guide to the Blockchain Revolution on our platform.
Potential Applications in Healthcare:
Blockchain technology finds its application in various aspects of healthcare, including:
- Data Management: Secure and efficient management of patient data.
- Drug Traceability: Ensuring the authenticity of drugs by tracking their journey from manufacturer to consumer.
- Clinical Trials: Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data in clinical trials.
- Billing and Insurance Claims: Streamlining the billing process and ensuring the accuracy of insurance claims.
| Application | Description | Challenges Addressed |
|---|---|---|
| Secure Data Management | Ensures the integrity and confidentiality of health data through cryptographic features and immutable records. | – Data Breaches – Unauthorized Access – Data Tampering |
| Streamlined Billing & Payments | Automates billing processes and facilitates instant payments through smart contracts, reducing the administrative burden and errors. | – Delayed Payments – Billing Errors – Fraud |
| Telemedicine & Remote Monitoring | Provides a secure framework for telemedicine consultations and remote monitoring of patients, ensuring data privacy and consent management. | – Data Privacy Concerns – Consent Management – Unauthorized Access |
| Research & Clinical Trials | Accelerates research and clinical trials through secure data sharing and collaboration, ensuring data integrity and compliance with regulatory requirements. | – Data Tampering – Lack of Transparency – Slow Research Progression |
| Supply Chain Management | Enhances traceability and accountability in healthcare supply chains, ensuring authenticity and timely delivery of medical supplies. | – Counterfeit Medicines – Supply Chain Inefficiencies – Lack of Traceability |
| Regulatory Compliance & Auditing | Facilitates real-time compliance checks and transparent auditing processes through immutable records and automated verification via smart contracts. | – Non-compliance Risks – Cumbersome Auditing Processes – Manual Compliance Checks |
| Global Health Data Exchange | Enables secure and standardized exchange of health data across borders, fostering global healthcare collaboration and research. | – Data Privacy Concerns – Lack of Standardization – Data Sharing Barriers |
| Personalized Medicine | Facilitates personalized treatment plans based on secure and immutable health data, advancing precision medicine. | – Data Security – Lack of Personalized Treatment Plans – Data Accessibility for Personalized Care Planning |
Health Data Management:
The Current Landscape:
The management of health data is a critical aspect of the healthcare system. It encompasses how patient data is collected, stored, and shared among different stakeholders. Currently, the healthcare sector faces challenges in ensuring the privacy, security, and accuracy of health data. Some of these challenges include:
- Data Silos: Patient data often exists in silos within different healthcare institutions, making it difficult to have a unified view of a patient’s health history.
- Data Security: With the rise of cyber-attacks, ensuring the security of sensitive health data is a pressing concern.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data over its entire lifecycle is crucial for delivering quality healthcare.
Blockchain as a Solution:
Blockchain technology can potentially resolve many of the existing issues related to health data management. Here’s how:
- Unified Patient Records: Blockchain can enable the creation of unified patient records that can be accessed by authorized individuals regardless of the institution they are affiliated with.
- Enhanced Data Security: The cryptographic security features of blockchain provide a robust shield against data breaches and unauthorized access. For a deeper dive into blockchain security, you can refer to Mastering Blockchain Security: From Basic Measures to Advanced Threats on our platform.
- Data Integrity: The immutability feature of blockchain ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered, thus ensuring data integrity.
Through blockchain, healthcare providers can have a holistic view of a patient’s medical history, which is crucial for delivering accurate and timely healthcare services.
Advantages Over Traditional Systems:
Comparing blockchain-based health data management systems with traditional systems highlights a range of advantages:
| Feature | Traditional Systems | Blockchain-Based Systems |
| Data Centralization | Centralized, leading to single points of failure. | Decentralized, eliminating single points of failure. |
| Data Access | Restricted due to data silos. | Unified access to authorized individuals. |
| Data Security | Vulnerable to cyber-attacks and unauthorized access. | Enhanced security through cryptographic features. |
| Data Integrity | Prone to errors and alterations. | Ensures data integrity through immutability. |
Blockchain technology, with its innate features, aligns well with the healthcare sector’s stringent requirements for data security, privacy, and integrity.
Supply Chain Traceability:
The Importance of Traceability:
In the healthcare sector, the traceability of drugs and medical supplies is not just about compliance; it’s a matter of public safety. Ensuring that medications and medical supplies are genuine and safe for use is crucial. The key aspects requiring traceability include:
- Authentication: Verifying the authenticity of drugs and medical supplies.
- Origin Verification: Tracing back the origin of drugs to ensure they comply with set standards.
- Recall Efficiency: In case of a faulty product, efficient recall processes to prevent harm to patients.
How Blockchain Enhances Traceability:
Blockchain technology can significantly improve the traceability of medical supplies and drugs. Here’s how:
- Immutable Record: Blockchain maintains an immutable record of all transactions, making it possible to trace the journey of a drug from manufacturer to consumer.
- Real-time Tracking: Real-time tracking of medical supplies ensures authenticity and compliance with healthcare standards.
- Efficient Recalls: In case of recalls, blockchain enables quicker identification of affected batches, thus minimizing risks to patients.
The traceability ensured by blockchain can also lead to cost savings by reducing counterfeit drugs and improving the efficiency of recall processes.
Comparative Analysis:
Comparing traditional traceability systems with blockchain-based systems highlights the advantages of blockchain technology in ensuring the traceability of drugs and medical supplies:
| Feature | Traditional Systems | Blockchain-Based Systems |
| Real-time Tracking | Limited or no real-time tracking. | Enables real-time tracking of supplies. |
| Data Integrity | Data can be altered or lost. | Immutability ensures data integrity. |
| Efficiency | Time-consuming recall processes. | Quick identification and recall of affected products. |
| Cost | High cost due to counterfeit drugs and inefficient recalls. | Cost savings through reduced counterfeits and efficient recalls. |
Blockchain technology’s ability to provide a transparent and immutable record of transactions makes it an invaluable tool for enhancing the traceability of drugs and medical supplies in the healthcare sector. For further insights into the capabilities of blockchain, the article The Ultimate Guide to Blockchain Technology: Everything You Need to Know in 2023 on our platform could be a helpful resource.
Patient Consent Management:
The Challenges:
Managing patient consent is a crucial yet complex aspect of healthcare operations. It involves obtaining, recording, and managing patients’ permissions regarding their healthcare treatment and data sharing. The challenges include:
- Informed Consent: Ensuring patients fully understand the implications of their consent.
- Record Keeping: Accurately recording and managing consent over time.
- Data Accessibility: Providing authorized individuals with timely access to consent data.
Blockchain for Consent Management:
Blockchain technology presents a robust solution for managing and documenting patient consent. Here’s how:
- Immutable Consent Records: Once recorded on the blockchain, consent data cannot be altered, ensuring accuracy and integrity.
- Smart Contracts: Utilize smart contracts to automate consent management, ensuring only authorized individuals have access to specific data based on pre-set conditions. For a better understanding of smart contracts, you can explore Smart Contracts Unveiled: Your Gateway to the Future of Digital Agreements on our platform.
- Real-Time Access: Blockchain facilitates real-time access to consent data for authorized individuals, streamlining healthcare operations.
Blockchain’s transparency and immutability features ensure the accuracy and integrity of consent data, making it a promising solution for patient consent management.
Benefits Over Traditional Systems:
Comparing traditional consent management systems with blockchain-based systems reveals a host of benefits:
| Feature | Traditional Systems | Blockchain-Based Systems |
| Record Integrity | Prone to alterations and inaccuracies. | Immutability ensures record integrity. |
| Automation | Manual processes for consent management. | Smart contracts automate consent processes. |
| Data Access | Delayed access to consent data. | Real-time access to consent data. |
The transition to blockchain-based consent management systems could significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of managing patient consent in healthcare.
| Stage | Traditional System Process | Blockchain-Based System Process |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Consultation | – Physician explains the need for consent. – Patient reads and understands the consent form. | – Physician explains the need for consent. – Patient reads and understands the digital consent form. |
| Consent Recording | – Patient signs the consent form. – Hospital staff manually enters consent data into the system. | – Patient digitally signs the consent form. – Consent data is automatically recorded on the blockchain. |
| Consent Management | – Updates or withdrawals require additional paperwork and manual system updates. – Access to consent information is through centralized, often siloed, systems. | – Updates or withdrawals are recorded as new transactions on the blockchain. – Access to consent information is decentralized and real-time. |
| Auditing and Compliance | – Manual auditing of consent forms and system data. – Compliance checks require significant time and manual effort. | – Automated auditing through smart contract verification. – Real-time compliance checks with transparent and immutable record-keeping. |
Billing and Payments:
Existing Challenges:
Billing and payments in healthcare are often seen as cumbersome due to various challenges that include:
- Billing Inaccuracies: Misinterpretations and errors in coding can lead to billing inaccuracies.
- Fraud: The healthcare sector is prone to fraudulent billing and insurance claims.
- Delayed Payments: Traditional billing systems often result in delayed payments, impacting the financial health of healthcare providers.
Blockchain’s Intervention:
Blockchain technology harbors the potential to streamline the billing process and reduce fraud through:
- Automated Billing: Smart contracts can automate billing processes, reducing human errors and speeding up the payment cycle.
- Fraud Detection: Blockchain’s immutable nature makes it easier to detect and prevent fraudulent activities by providing a transparent and unalterable record of transactions.
- Instant Payments: Blockchain can facilitate instant payments, ensuring healthcare providers receive timely compensation for their services.
By addressing the core issues surrounding billing and payments, blockchain can significantly improve the financial workflow in healthcare.
Comparative Assessment:
A comparative assessment between traditional and blockchain-based billing systems accentuates the advantages of blockchain technology:
| Feature | Traditional Systems | Blockchain-Based Systems |
| Billing Accuracy | Prone to human errors leading to inaccuracies. | Automated billing via smart contracts improves accuracy. |
| Fraud Prevention | Limited fraud detection capabilities. | Enhanced fraud detection due to immutability. |
| Payment Speed | Delayed payments are common. | Instant payments facilitated by blockchain. |
Blockchain technology’s inherent features like immutability, transparency, and the capability for smart contracts make it a viable solution for overcoming challenges in healthcare billing and payments. For a deeper understanding of smart contracts, you might find Smart Contracts Unveiled: Your Gateway to the Future of Digital Agreements to be a valuable resource.
Research and Clinical Trials:
The Significance:
Research and clinical trials are the pillars of advancing healthcare. They are crucial for the development of new treatments and understanding diseases. However, these areas face challenges such as:
- Data Integrity: Ensuring that the data collected is accurate and hasn’t been tampered with is crucial for the validity of research.
- Data Sharing: Secure and efficient data sharing among researchers can accelerate discoveries but poses a challenge due to privacy concerns.
- Patient Recruitment: Efficient patient recruitment and retention are essential for the success of clinical trials.
Blockchain’s Potential:
Blockchain technology can address these challenges in the following ways:
- Ensuring Data Integrity: Blockchain’s immutability ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of research data.
- Secure Data Sharing: Blockchain can facilitate secure and transparent data sharing among researchers, ensuring privacy while fostering collaboration.
- Streamlined Patient Recruitment: Smart contracts on a blockchain can automate and streamline patient recruitment and consent management processes.
Blockchain not only enhances the integrity and security of data in research and clinical trials but also fosters a collaborative environment by enabling secure data sharing.
Comparative Insights:
Comparing traditional methods with blockchain-based methods in research and clinical trials gives us the following insights:
| Feature | Traditional Methods | Blockchain-Based Methods |
| Data Integrity | Risk of data tampering and loss. | Immutability ensures data integrity. |
| Data Sharing | Limited due to privacy concerns. | Secure and transparent data sharing. |
| Patient Recruitment | Manual processes, time-consuming. | Streamlined through smart contracts. |
Blockchain technology’s core features of immutability, transparency, and the utilization of smart contracts significantly contribute to overcoming the challenges faced in research and clinical trials. For more insights into blockchain’s foundational principles, The Ultimate Guide to Blockchain Technology: Everything You Need to Know in 2023 on our platform could be a helpful resource.
Regulatory Compliance and Auditing:
Necessity of Compliance and Auditing:
In the healthcare sector, adhering to regulatory compliance and conducting regular audits is not just about fulfilling legal obligations—it’s about ensuring patient safety and maintaining trust. Key areas include:
- Privacy Compliance: Adhering to laws and regulations that protect patient privacy.
- Financial Auditing: Ensuring financial operations comply with the standards.
- Quality Assurance: Verifying that healthcare delivery meets the required quality standards.
Blockchain’s Role:
Blockchain can significantly simplify the compliance and auditing processes in healthcare:
- Immutable Records: Blockchain’s immutable nature ensures that the records cannot be altered once saved, providing a reliable base for auditing and compliance checks.
- Automated Compliance: Smart contracts can automate many compliance processes, ensuring real-time adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Transparent Auditing: Blockchain’s transparency enables straightforward auditing processes, making it easier to comply with regulatory requirements.
Blockchain technology provides a framework for transparent and immutable record-keeping, which is essential for regulatory compliance and auditing in healthcare.
Comparative Analysis:
The comparison between traditional methods and blockchain-based methods for regulatory compliance and auditing reveals:
| Feature | Traditional Methods | Blockchain-Based Methods |
| Record Integrity | Records can be altered, leading to unreliable audits. | Immutable records ensure reliable audits. |
| Compliance Efficiency | Manual compliance checks are time-consuming. | Automated compliance via smart contracts. |
| Auditing Transparency | Auditing process can be cumbersome and opaque. | Transparent and straightforward auditing process. |
The benefits of blockchain for regulatory compliance and auditing are substantial, promising a more transparent and efficient process. For a comprehensive understanding of how blockchain operates, How Does Blockchain Work: A Comprehensive Guide to the Blockchain Revolution on our platform could provide valuable insights.
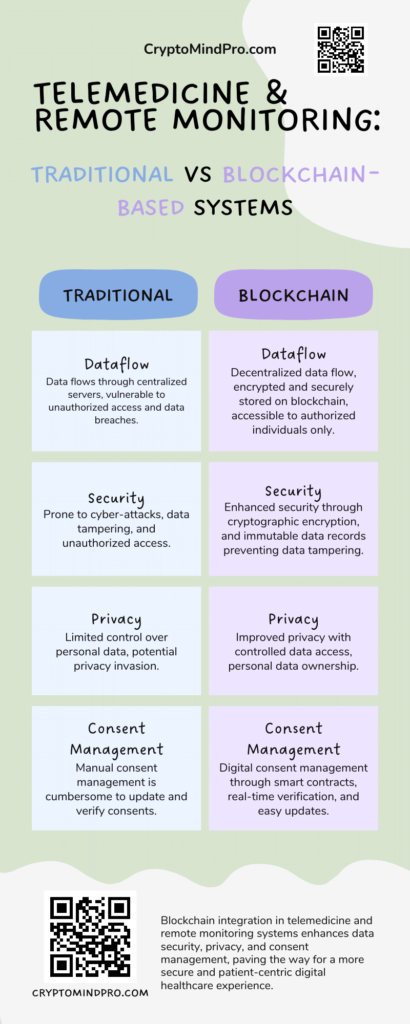
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring:
Rise of Digital Healthcare:
Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring have seen a significant rise, especially catalyzed by the COVID-19 pandemic. These digital health solutions offer:
- Accessibility: Healthcare access to individuals in remote or underserved areas.
- Convenience: Reduced need for in-person visits, saving time and resources.
- Early Intervention: Remote monitoring allows for early detection and intervention in potential health issues.
Blockchain’s Contribution:
Blockchain can play a vital role in addressing challenges and enhancing telemedicine and remote monitoring:
- Data Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic features ensure the security of sensitive health data transmitted and stored digitally.
- Patient Privacy: Control over data access can be maintained through blockchain, ensuring patient privacy.
- Consent Management: As discussed earlier, blockchain can manage patient consent, ensuring authorized access to medical data for telemedicine consultations.
Blockchain technology can provide a secure and efficient framework for the rapidly evolving telemedicine and remote patient monitoring domains.
Comparative Advantages:
Comparing traditional telemedicine systems with blockchain-integrated systems highlights blockchain’s benefits:
| Feature | Traditional Systems | Blockchain-Integrated Systems |
| Data Security | Vulnerable to breaches and unauthorized access. | Enhanced security through cryptographic features. |
| Patient Privacy | Privacy can be compromised due to weak control over data access. | Improved privacy with controlled data access. |
| Consent Management | Manual processes, prone to errors. | Streamlined consent management through smart contracts. |
Blockchain technology’s decentralized nature and immutability provide a robust foundation for secure and efficient telemedicine and remote monitoring services. For further exploration on blockchain’s security features, the article Mastering Blockchain Security: From Basic Measures to Advanced Threats on our platform could provide valuable insights.
Future Prospects:
Unlocking New Horizons:
The integration of blockchain technology in healthcare is still in its nascent stages, yet the potential is vast. As the technology matures and more use cases emerge, blockchain could revolutionize various facets of healthcare, including:
- Personalized Medicine: Tailored treatment plans based on a person’s genetic makeup and health data.
- Global Health Data Exchange: Secure and standardized exchange of health data across borders, improving global healthcare collaboration.
- Healthcare Supply Chain Optimization: Enhanced traceability and efficiency in healthcare supply chains, reducing costs and ensuring authenticity.
Challenges Ahead:
Despite the potential benefits, several challenges need to be addressed for successful blockchain integration in healthcare:
- Technology Understanding: There’s a need for a deeper understanding and education regarding blockchain among healthcare professionals.
- Scalability: Blockchain solutions need to be scalable to handle the vast amount of data generated in healthcare.
- Regulatory Framework: Establishing a regulatory framework that supports blockchain adoption while ensuring patient privacy and data security.
Navigating the Path Forward:
Overcoming these challenges requires collaborative efforts from healthcare professionals, blockchain experts, and policymakers. It’s crucial to:
- Educate and Train: Equip healthcare professionals with the necessary knowledge and skills regarding blockchain technology.
- Develop Scalable Solutions: Focus on developing scalable blockchain solutions that cater to the healthcare sector’s unique requirements.
- Engage Policymakers: Engage with policymakers to establish a supportive regulatory framework for blockchain adoption in healthcare.
The road towards blockchain integration in healthcare may be steep, but the potential benefits for patient care, data security, and operational efficiency are substantial. For a broader perspective on blockchain technology, the article The Ultimate Guide to Blockchain Technology: Everything You Need to Know in 2023 on our platform could be a valuable resource.
Unveiling the Future: The Blockchain Revolution in Healthcare
The voyage into the realms of blockchain technology unveils a horizon brimming with promise for the healthcare industry. As we peel back the layers of conventional healthcare systems, the potential of blockchain emerges as a beacon of hope, capable of addressing longstanding challenges—from securing sensitive health data to streamlining complex processes.
The path ahead is not devoid of challenges, yet the rewards are palpable. The fusion of blockchain’s indelible ledger, decentralized framework, and the automation prowess of smart contracts, with the healthcare sector’s meticulous data management and patient care, is a narrative of empowerment and innovation. It’s about rewriting the script of healthcare operations to resonate with the ethos of security, transparency, and efficiency.
The discourse around blockchain in healthcare is no longer confined to theoretical contours but is gaining a tangible form. As healthcare practitioners, blockchain aficionados, and policymakers converge on the common ground of aspiration for better healthcare, a new era beckons.
The onus is on us to continue the exploration, to foster a culture of learning, innovation, and collaboration. The fusion of blockchain and healthcare is a journey, not a destination. It’s about nurturing a dynamic ecosystem that evolves with every challenge and every breakthrough.
As we stand at the cusp of this technological renaissance, the prospect of delivering enhanced patient care, bolstered by the robust framework of blockchain, is not just an imaginative vision, but a reachable reality. The blueprint for a blockchain-integrated healthcare paradigm is gradually unfolding, and as it does, the anticipation of a new dawn in healthcare keeps us propelled towards the goal.
Let’s embrace the journey with an open mind, ready to unlock the myriad possibilities that blockchain brings to the table. The narrative of blockchain in healthcare is being written with each passing day, and it’s a story of hope, innovation, and a relentless pursuit of better healthcare for all.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
| Question | Answer |
| What is blockchain technology? | Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that records transactions across many computers in a way that ensures the security and integrity of the data. |
| How can blockchain benefit healthcare? | Blockchain can enhance data security, ensure the integrity of medical records, streamline billing processes, improve supply chain traceability, manage patient consent, and foster secure telemedicine practices. |
| Is blockchain secure for healthcare data? | Yes, blockchain’s cryptographic features and immutable nature make it a highly secure technology for managing healthcare data. |
| How can blockchain improve patient privacy? | Blockchain allows for controlled access to patient data, ensuring only authorized individuals can access specific information, thus improving patient privacy. |
| What are smart contracts and how are they relevant to healthcare? | Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They can automate various healthcare processes like billing, consent management, and data access authorization, improving efficiency and compliance. |
| Are there any real-world implementations of blockchain in healthcare? | Yes, several projects and organizations are exploring or have implemented blockchain solutions in healthcare for use cases like supply chain management, patient data management, and clinical trials. |
| What are the challenges to blockchain adoption in healthcare? | Challenges include a lack of understanding of blockchain technology, scalability issues, and the need for a supportive regulatory framework. |
| How can I learn more about blockchain in healthcare? | Exploring online resources, reading industry reports, attending webinars, and networking with industry experts are great ways to learn more about blockchain in healthcare. |
| Can blockchain facilitate telemedicine? | Yes, blockchain can enhance data security, patient privacy, and consent management in telemedicine, making it a more secure and efficient practice. |
| What’s the future of blockchain in healthcare? | The future is promising with the potential for blockchain to revolutionize various facets of healthcare, although it requires overcoming certain challenges and fostering a conducive environment for blockchain adoption. |




